Think about what apps and websites do with your information. This year, Apple’s iOS 15 and Google’s Android 12 updated their privacy settings to give you more information and options when a site or service wants to use personal information like your location or what your computer clicks on. Here is a quick look at how these settings can be changed.
Table of Contents
How to Use Your Phone’s Privacy Protection Tools?
System Settings
On iOS or Android, you can tap or speak to open the Settings app and then choose Privacy. There are many screens, buttons, and keys that let you choose which apps can use the phone’s hardware, like the microphone, and software, like your contacts list.
Android 12 has a privacy panel that shows what apps have been doing and gives quick ways to control what information Google gets and stores in a user’s Google Account.
Apple and Google have both talked about how they use your information if you’re interested. Keep in mind that deleting your online tracks and location information could change how your free apps work and that many news and culture websites use tracking software.
But if you want to have more power over your information, here are some things to think about.
Location
You can use your phone’s location services to find out exactly where you are on a map. This can help you figure out things like how to get somewhere. But in newer versions of iOS and Android, you can share a general idea of where you are instead of your exact location. Because of this, you are a little bit safer.
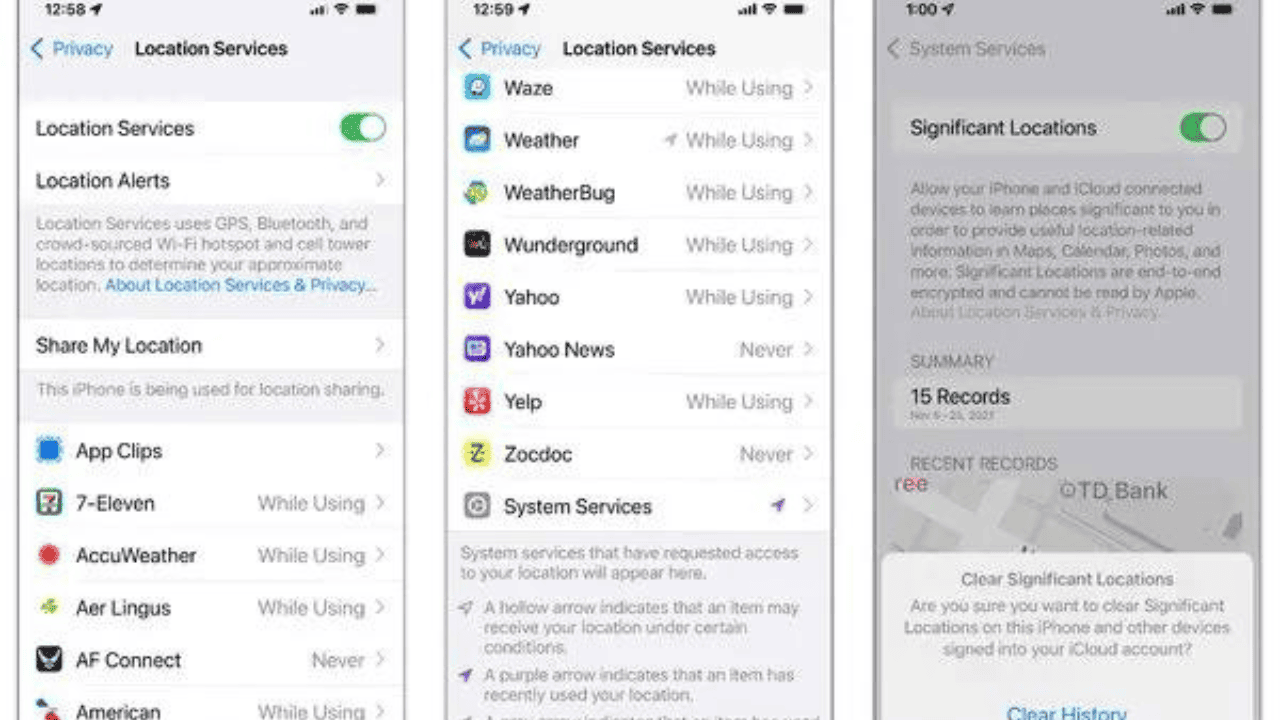
On an iOS 15 device, open the Settings app and click on Privacy, then Location Services, and finally System Services. Here, you can turn on or off location services and decide when and which third-party apps, like Google’s, can use your information.
Scroll all the way to the bottom of the list and click on System Services to see how your iPhone uses your location, such as by keeping track of “significant locations” like your home address. You can turn it off or get rid of the past if you don’t like it.
Open the Settings app on an Android 12 phone and tap Location. This will open the settings so you can see which apps can access your location. If you want to make more changes, tap Location Services.
You can also change the way your phone remembers your current location. Google’s business plan includes giving you ads and services that are tailored to you based on the information you give them.
Apps and Ads
Apple’s App Tracking Transparency tool lets you know when an app wants to track what you do online, usually to show you more relevant ads. In iOS 15, go to Settings, then Privacy, and then Tracking to get to the settings.
Apple’s advertising site says it doesn’t share information that could be used to find out who you are, but you can turn off these ads in the Privacy settings under “Apple Advertising.” When you open the Settings menu on Android 12 and click on Privacy, you can change a lot of settings.
One of these is the Ads choice, which lets you delete your Advertising ID so that you no longer see ads that are about you. Google said this month that if you haven’t used an app in a while, it will immediately lose access to your phone.
Web
Using cookies and other code that keeps track of what you do online, marketers and advertisers have been able to follow you through your computer for decades. Safari’s Private viewing and Chrome’s Incognito mode keep your viewing history from being saved, but they don’t do much to stop browser crawlers.
Apple’s App Tracking Transparency tool lets you know when an app wants to track what you do online, usually to show you more relevant ads. In iOS 15, go to Settings, then Privacy, and then Tracking to get to the settings.
Even though Apple’s advertising platform says it doesn’t share information that could be used to figure out who you are, you can turn these ads off in the Privacy settings by going to Apple Advertising.
Apple’s Safari program has tools that can stop tracking. Go to Settings, then Safari, and scroll down to Privacy & Security to use them. You can tell sites not to track you in the Privacy and Security section of Google’s Chrome browser, though some still do.
You can also get rid of a lot of computer bugs by using a safety-focused app like Brave or DuckDuckGo. The company just recently said that the Android version of DuckDuckGo’s Privacy Browser will have an App Tracking Protection Tool and an email protection tool. The public is trying these out right now.
A “tracking pixel” may be used by advertisers in some messages. This is a secret picture that tells the writer, among other things, when you open the message. With Apple’s iOS 15, you can use a tool to stop text bots. Go to Settings, then Mail, then Privacy Protection, and then tap on Protect Mail Activity to turn it on Protect Mail Activity.
You can stop the Gmail app for Android or iOS from taking pictures and giving notifications as soon as you do this. Just tap the Menu icon in the upper left corner, choose Settings, then your account name, and in the Images section, choose “Ask before displaying external images…” And email lists that send you things you don’t want can always be stopped or unsubscribed from.
Why Must We Use These Privacy Protection Tools?
There are things that could go wrong with our phones, and we need to be aware of them. As more and more people use their phones to talk, shop, and use social media, it’s important to be aware of the following risks:
Hackers go after both people and businesses to get their hands on private information without permission. This is called stealing info. When our phones are stolen, the wrong people can get access to private information like passwords, bank information, and private conversations.
Malicious software like spyware and malware pose a big threat to our privacy. Malware can get on our devices through apps, emails, and websites that have been hacked. This lets hackers see what we do, steal our personal information, and even take control of our gadgets from far away.
Many of the apps on our computers want to know where we are, which makes us worry about our privacy and safety. Companies can learn a lot about our habits, likes, and behavior by keeping track of where we go, which could put our privacy at risk.
Phishing scams are tricks that try to get people to give away private information, like passwords or credit card numbers, that they shouldn’t. Cybercriminals often use well-thought-out emails, texts, and websites to trick people into giving them their personal information.
Conclusion
In the digital world of today, it’s very important to keep your smartphone private. By learning the risks to privacy, using built-in privacy tools, and following best practices, you can keep your personal information much safer. When you use your phone every day, be aware, keep it updated, and put safety first. With these steps in place, you can use your smartphone quickly and enjoy its benefits without thinking about your privacy being violated.